<SVM (Hinge loss) >
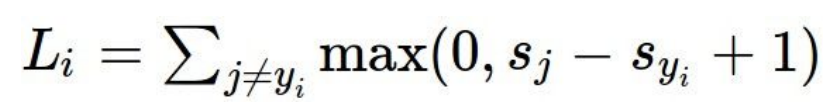
# 코드 구현
def L_i_vectorized(x, y, W):
scores = W.dot(x)
margins = np.maximum(0, scores - scores[y] + 1)
margins[y] = 0
loss_i = np.sum(margins)
return loss_i
- Data loss + Regularization

- Data loss : Model predictions should match training data
- Regularization : Model should be "simple", so it works on test data(정규화)
- L2 regularization
- L1 regularization
- Elastic net(L1+L2)
- Max norm regularization
- Dropout


<Softmax (cross-entropy loss)>
- unnormalized log probabilities → unnormalized probabilities → probabilities

<Recap>

<Optimization>
- Loss를 minimize하는 weight를 찾아가는 과정
- regularization loss는 weight에만 영향을 받음
- 미분을 통해 구할 수 있음
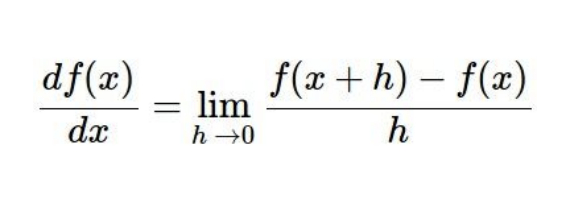
- Numerical gradient : 쓰기 쉽지만, 느리고 근사치를 낸다.
- Analytic gradient : 정확하고 빠르지만 오류가 발생하기 쉽다.
# Vanilla Gradient Descent
while True :
weights_grad = evaluate_gradient(loss_fun, data, weights)
weights += step_size * weights_grad #perform parameter update
<Stochastic Gradientv Descent(SGD)>
- 확률적 경사 하강법은 실제 기울기를 추정한 값으로 대체하여 목적함수를 최적화하기 위한 방법

#Vanilla Minibatch Gradient Descent
while True :
data_batch = sample_training_data(data,256) # sample 256 examples
weights_grad = evaluate_gradient(loss_fun, data_batch, weights)
weights += -step_size * weights_grad # perform parameter update'데이터 > 딥러닝' 카테고리의 다른 글
| CS231n_Lecture5:Convolutional Neural Networks (0) | 2022.11.01 |
|---|---|
| CS231n_Lecture4:Introduction to Neural Networks (0) | 2022.11.01 |
| CS231n_Lecture1, 2:Image Classification pipeline (0) | 2022.09.20 |
| Chapter 07-1 인공신경망 (0) | 2022.07.25 |
| 2.1 신경망 표현 (0) | 2021.07.29 |


